Artificial
Intelligence 2E
foundations of computational agents
The third edition of Artificial Intelligence: foundations of computational agents, Cambridge University Press, 2023 is now available (including full text).
14.2.2 Graphical Representations
You can interpret the relation in terms of a directed graph, where the relation
is depicted with and as nodes with an arc labeled with between them. Such a graph is called a semantic network or knowledge graph. There is a straightforward mapping form a knowledge graph into a knowledge base using the relation, as in the following example.
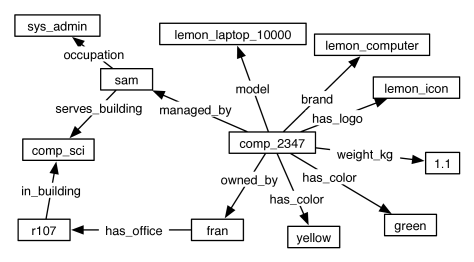
Example 14.7.
Figure 14.1 shows a semantic network for the delivery robot showing the sort of knowledge that the robot might have about a particular computer in a university department. Some of the knowledge represented in the network is
The network also shows how the knowledge is structured. For example, it is easy to see that computer number is owned by someone (Fran) whose office (r107) is in the building. The direct indexing evident in the graph can be used by humans and machines.
This graphical notation has a number of advantages:
-
•
It is easy for a human to see the relationships without being required to learn the syntax of a particular logic. The graphical notation helps the builders of knowledge bases to organize their knowledge.
-
•
You can ignore the labels of nodes that just have meaningless names – for example, the name in Example 14.6, or in Figure 14.1. You can just leave these nodes blank and make up an arbitrary name if you must map to the logical form.